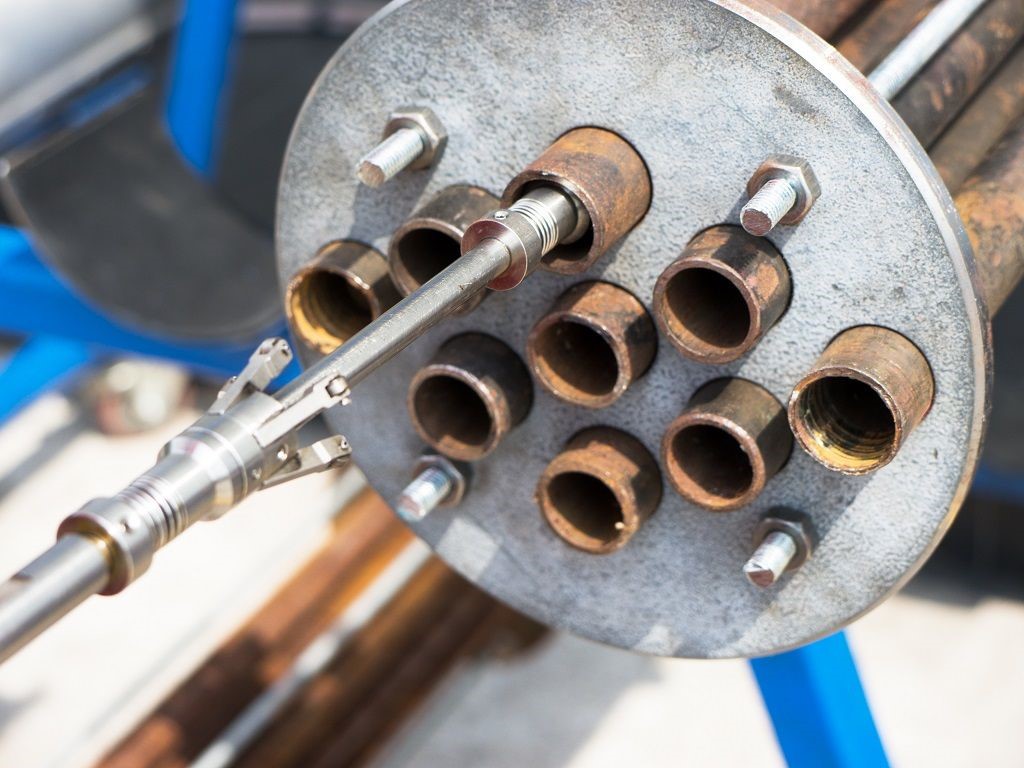



IRIS is an ultrasonic method used for the non-destructive testing of pipes and tubes.
Many plant operators in the oil & gas and power generation industries are faced with the challenges of maximizing the efficiency and life expectancy of their assets but without sacrificing safety and reliability. Therefore, accurate inspection of vital components such as pipes and tubes is crucial to ensuring the integrity of the plant.
Internal Rotary Inspection System (IRIS) can detect corrosion, pitting and wall loss and is most commonly used for tube inspection in boilers, heat exchangers, air coolers and feed water heaters. It is particularly versatile as it is suitable for both ferrous and non-ferrous materials, and IRIS can be used on a wide range of tube diameters and wall thickness.
An IRIS probe is inserted into a tube flooded with water. The probe is fitted with a transducer that generates an ultrasonic pulse along a path parallel to the axis of the tube. A rotating mirror directs the ultrasonic pulse into the tube wall. The mirror is driven by a small turbine that is rotated by the pressure of water pumped into the tube. The ultrasound pulses are reflected by the inner-diameter (ID) wall and outer-diameter (OD) wall of the tube and the time-of-flight difference between the two diameters is used to calculate the wall’s thickness. As the IRIS probe is pulled, the spinning motion of the mirror results in a helical scan path ensuring full coverage of the tube.
Merits of IRIS Tube Inspection
+91 63839 92501
admin@u-sonix.com